Understanding the Operation of Households and Businesses: The Two Basic Economic Units
In any economy, households and businesses serve as the fundamental building blocks that drive economic activity. These two basic economic units interact within markets, making decisions that influence the allocation of resources, production of goods and services, and overall economic well-being. This article explores how households and businesses operate, their roles in the economy, and their interdependent relationships.
The Role of Households
Definition and Function
Households are economic units that consist of individuals or groups of people living together and making joint decisions about consumption, labor, and savings. They are the primary consumers of goods and services and provide labor to businesses.
Consumption Decisions
Households make consumption decisions based on their preferences, income, and prices of goods and services. These decisions are influenced by:
- Income: The amount of money households earn from wages, salaries, investments, and other sources.
- Preferences: The tastes and preferences of household members, which determine their demand for various goods and services.
- Prices: The cost of goods and services, which affects the quantity demanded.
Households allocate their income to maximize utility, the satisfaction derived from consuming goods and services. They must decide how much to spend on necessities (such as food, housing, and healthcare) versus discretionary items (such as entertainment and vacations).
Labor Supply
Households also supply labor to the market. The decision to work and the amount of labor supplied depend on:
- Wages: The compensation received for labor, which influences the willingness to work.
- Opportunity Cost: The value of the next best alternative use of time, such as leisure or education.
- Preferences and Constraints: Personal preferences for work-life balance and constraints such as family responsibilities.
By supplying labor, households earn income that they can then use for consumption and savings.
Savings and Investment
Households decide how much of their income to save and invest. Savings provide a safety net for future uncertainties and can be invested to earn returns, contributing to capital formation in the economy. The level of savings is influenced by:
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates provide greater returns on savings, encouraging more savings.
- Future Expectations: Expectations about future income, inflation, and economic conditions impact savings decisions.
- Lifecycle Needs: Different stages of life, such as retirement planning, affect the propensity to save.
The Role of Businesses
Definition and Function
Businesses are economic units that produce goods and services to sell in the market. They aim to maximize profits by efficiently using resources and responding to consumer demand.
Production Decisions
Businesses decide what goods and services to produce based on:
- Market Demand: Understanding consumer preferences and demand patterns to produce goods and services that are likely to sell.
- Costs of Production: The costs associated with labor, raw materials, capital, and technology influence production decisions. Businesses strive to minimize costs to maximize profits.
- Technology: Technological advancements can improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Profit Maximization
The primary goal of businesses is to maximize profits, which is achieved by:
- Revenue Generation: Selling goods and services at prices that consumers are willing to pay.
- Cost Management: Controlling and reducing production and operational costs.
- Market Competition: Competing with other businesses to attract customers and gain market share.
Investment and Growth
Businesses invest in capital goods, technology, and human resources to improve production capabilities and expand operations. Investment decisions are influenced by:
- Expected Returns: The potential profitability of investments.
- Interest Rates: The cost of borrowing money to finance investments.
- Economic Conditions: The overall economic environment, including market conditions and government policies.
Interdependence of Households and Businesses
Circular Flow of Economic Activity
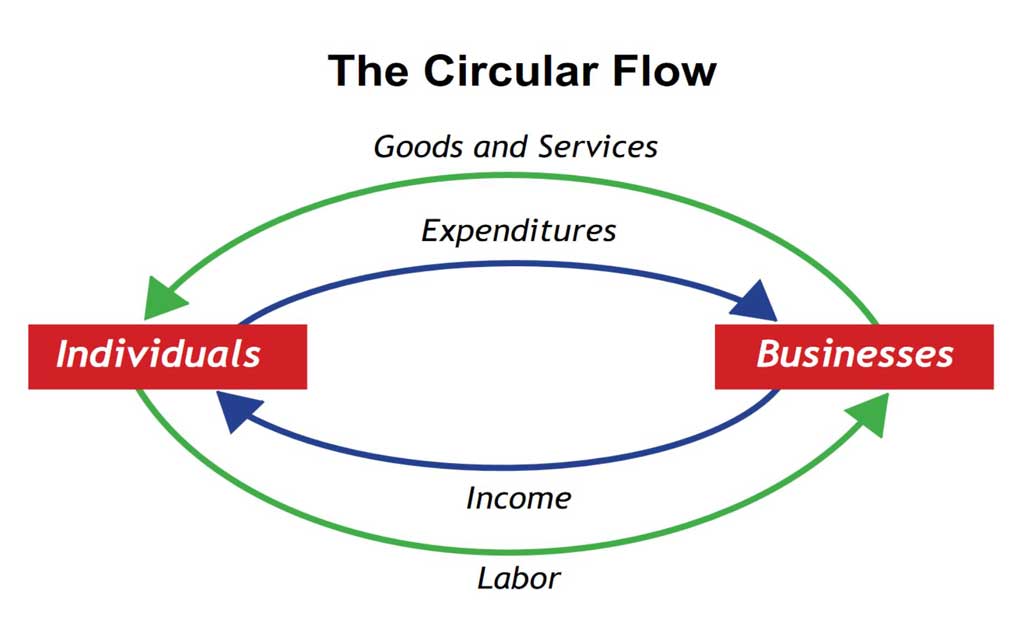
Households and businesses are interconnected through the circular flow of economic activity:
- Households provide labor to businesses and receive wages in return.
- Businesses produce goods and services that households buy using their income.
- Households save and invest their income, providing capital for businesses to expand and innovate.
- Businesses invest in production and pay wages to households, continuing the cycle.
Market Equilibrium
The interaction between households and businesses determines market equilibrium:
- Supply and Demand: Businesses supply goods and services based on production capabilities and costs, while households demand goods and services based on preferences and income.
- Price Mechanism: Prices adjust to balance supply and demand. If demand exceeds supply, prices rise, incentivizing businesses to produce more. If supply exceeds demand, prices fall, encouraging households to buy more.
Economic Growth and Stability
The efficient operation of households and businesses is crucial for economic growth and stability:
- Consumption and Investment: Household consumption drives demand, while business investment fuels production and innovation.
- Employment and Income: Businesses provide employment opportunities, generating income for households, which in turn supports consumption and savings.
- Resource Allocation: The decisions of households and businesses regarding consumption, production, and investment lead to the efficient allocation of resources in the economy.
Conclusion
Understanding how households and businesses operate is essential for grasping the dynamics of any economy. Households play a crucial role as consumers and labor suppliers, while businesses drive production and innovation. Their interdependent relationship, mediated through markets and prices, ensures the continuous flow of economic activity. By analyzing the behavior and decisions of these two basic economic units, we gain insights into the mechanisms that underpin economic growth, stability, and development. Whether you are a student, policymaker, or business professional, appreciating the interplay between households and businesses is key to understanding and influencing economic outcomes.
